Small Business Health Insurance Explained: A Guide for Startups
As Small Business Health Insurance Explained: A Guide for Startups takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of small business health insurance, covering everything from types of plans to cost management strategies.
Overview of Small Business Health Insurance
Small business health insurance refers to a type of health coverage provided by employers to their employees, typically in companies with fewer than 50 employees. It helps cover medical expenses and promotes the well-being of employees.
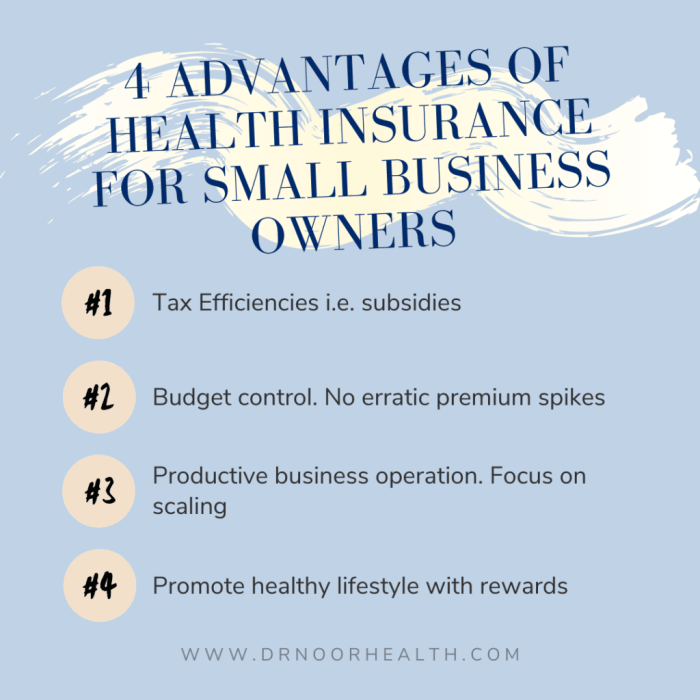
Offering health insurance is crucial for startups as it plays a significant role in attracting and retaining top talent. It demonstrates a commitment to employee welfare and can improve job satisfaction and loyalty within the organization.
Importance of Providing Health Insurance
- Enhances Recruitment: By offering health insurance, startups can attract high-quality candidates who value comprehensive benefits packages.
- Employee Retention: Providing health coverage can increase employee retention rates as workers are more likely to stay with a company that invests in their well-being.
- Boosts Morale: Access to health insurance can enhance employee morale, productivity, and overall job satisfaction within the organization.
Benefits of Providing Health Insurance vs. Not Providing It
- Providing Health Insurance:
- Attracts Top Talent: Comprehensive benefits packages, including health insurance, can attract skilled employees.
- Employee Wellness: Health coverage promotes the well-being of employees and ensures they have access to necessary medical care.
- Legal Compliance: Some jurisdictions require employers to provide health insurance, ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Not Providing Health Insurance:
- Difficulty in Recruitment: Lack of health benefits may deter potential candidates looking for comprehensive compensation packages.
- Higher Turnover: Without health insurance, employees may seek opportunities with better benefits, leading to higher turnover rates.
- Healthcare Costs: Employees without insurance may delay seeking medical care, potentially resulting in higher healthcare costs down the line.
Types of Small Business Health Insurance Plans
When it comes to providing health insurance for your small business, there are several types of plans to consider. Each plan has its own set of features, coverage options, and costs, so it's important to understand the differences before making a decision.
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
An HMO plan typically requires employees to select a primary care physician (PCP) who will coordinate all of their healthcare needs. Referrals are usually needed to see specialists, and services outside of the network may not be covered. While these plans often have lower premiums, they can limit flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
PPO plans offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, allowing employees to see specialists without a referral. These plans typically have higher premiums but provide coverage for out-of-network services, albeit at a higher cost. Employees can still receive some coverage for services outside the network.
High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP)
HDHPs come with higher deductibles but lower premiums compared to other plans. They are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) to help employees cover out-of-pocket costs. These plans can be a good option for businesses looking to offer coverage while managing costs.
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
EPO plans are similar to PPOs but do not cover any out-of-network services, except in emergencies. These plans may have lower premiums compared to PPOs but still offer flexibility in choosing healthcare providers within the network.
Point of Service (POS) Plan
POS plans combine features of HMOs and PPOs, allowing employees to choose whether to see providers in or out of the network. While referrals are generally required for specialists, employees have more flexibility in their healthcare choices compared to traditional HMO plans.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Health Insurance Plan
When small business owners are selecting a health insurance plan for their employees, several key factors come into play. These factors can greatly impact the decision-making process and the overall satisfaction of both the employer and employees.
Company Size
The size of the company plays a significant role in determining the type of health insurance plan that would be most suitable. Smaller businesses may opt for more affordable options with limited coverage, while larger companies may have the resources to provide comprehensive plans with more benefits.
Budget Constraints
Budget is a crucial factor when choosing a health insurance plan. Small business owners need to balance offering competitive benefits to attract and retain top talent while also staying within their financial means. It's essential to find a plan that provides adequate coverage without breaking the bank.
Employee Needs
Understanding the specific needs of your employees is essential when selecting a health insurance plan. Consider factors such as age demographics, existing health conditions, and family size to ensure that the chosen plan meets the diverse needs of your workforce.
Reviewing Coverage Options
Before making a decision, it's important to carefully review the coverage options offered by different health insurance plans. Consider the range of services covered, including preventive care, prescription medications, and specialist visits, to ensure that the plan aligns with the healthcare needs of your employees.
Network Providers
Another critical factor to consider is the network of healthcare providers included in the insurance plan. Ensure that the plan offers access to a wide network of doctors, hospitals, and specialists to provide employees with ample choices for their healthcare needs.
Premiums and Cost-Sharing
Compare the premiums and cost-sharing requirements of different health insurance plans to determine the most cost-effective option for your business
Navigating Small Business Health Insurance Regulations
When it comes to offering health insurance as a small business, there are certain regulations and requirements that you need to be aware of to ensure compliance. Understanding these key regulations is crucial for the successful implementation of a health insurance plan for your employees.
Affordable Care Act (ACA) Impact on Small Business Health Insurance
The Affordable Care Act, also known as Obamacare, has had a significant impact on small business health insurance. One of the key provisions of the ACA is the employer mandate, which requires businesses with 50 or more full-time employees to offer health insurance or face penalties.
Additionally, the ACA established health insurance marketplaces where small businesses can shop for group health insurance plans.
Tax Credits and Incentives for Small Businesses
As a small business offering health insurance, you may be eligible for tax credits and incentives to help offset the costs of providing coverage to your employees. The Small Business Health Care Tax Credit is available to businesses with fewer than 25 full-time employees who meet certain criteria.
This credit can cover up to 50% of the employer's contribution toward employee premiums.
Customizing Health Insurance Benefits for Employees
When it comes to providing health insurance benefits for employees, customization is key to meeting the diverse needs of your workforce. By tailoring your health insurance offerings, you can ensure that your employees have access to the coverage that best suits their individual circumstances.
Role of Voluntary Benefits
Voluntary benefits such as dental, vision, and mental health coverage can play a crucial role in enhancing your overall health insurance package. These additional benefits can provide employees with coverage for services that may not be included in a standard health insurance plan.
- Offering dental insurance can help employees maintain good oral health, which is essential for overall well-being.
- Providing vision insurance can cover the cost of eye exams, glasses, and contact lenses, ensuring that employees have access to proper vision care.
- Including mental health coverage can support employees' mental well-being by providing access to counseling services and therapy.
Wellness Programs for Employee Health
Wellness programs are a great way to complement your health insurance offerings and promote a culture of health and well-being in the workplace. These programs can encourage employees to adopt healthy behaviors and lifestyles, ultimately leading to improved overall health and reduced healthcare costs.
- Implementing fitness challenges or gym membership discounts can motivate employees to stay active and prioritize their physical health.
- Offering healthy eating initiatives or nutrition counseling can help employees make better food choices and improve their dietary habits.
- Providing mental health resources such as stress management workshops or meditation sessions can support employees' mental well-being and reduce workplace stress.
Cost Management Strategies for Small Business Health Insurance
When it comes to managing costs for small business health insurance, there are several strategies that can help businesses save money and provide valuable benefits to employees. One of the key aspects of cost management is finding the right balance between affordability and comprehensive coverage.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs)
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are tax-advantaged accounts that allow employees to contribute pre-tax dollars to cover qualified medical expenses. These funds can be used to pay for deductibles, copayments, and other out-of-pocket costs.
- Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) are similar to HSAs but have some key differences. FSAs also allow employees to contribute pre-tax dollars for medical expenses, but funds must be used within the plan year or a grace period.
- Both HSAs and FSAs can help employees manage healthcare costs while providing tax benefits for both the employer and the employee.
Negotiating with Insurance Providers and Adjusting Coverage Levels
- One effective cost-saving strategy is to negotiate with insurance providers for better rates or discounts. Small businesses can leverage their bargaining power to secure more affordable premiums or additional benefits.
- Adjusting coverage levels based on the needs of employees can also help manage costs. By offering tiered plans or customizable options, businesses can tailor their health insurance benefits to match their budget and the preferences of their workforce.
- Regularly reviewing and optimizing health insurance plans can ensure that businesses are getting the best value for their investment while providing valuable coverage to employees.
Last Point
In conclusion, Small Business Health Insurance Explained: A Guide for Startups offers valuable insights for entrepreneurs navigating the complexities of health insurance. It's a roadmap to making informed decisions that benefit both the company and its employees.
Helpful Answers
What are the key benefits of providing health insurance for startups?
Providing health insurance can attract top talent, improve employee retention, and enhance overall morale and productivity within the company.
How does the size of a company impact the selection of a health insurance plan?
The size of a company can influence the available options, costs, and flexibility in tailoring the plan to meet employee needs. Larger companies may have more bargaining power with insurers.
What cost-saving strategies can small businesses implement for health insurance?
Small businesses can explore options like health savings accounts (HSAs) and negotiate with insurance providers to lower costs. Additionally, adjusting coverage levels based on employee needs can help manage expenses.




